Introduction
Sensitization in austenitic steel refers to the process of making steel more resistant to corrosion by increasing its resistance to corrosion-inducing environments. This is usually done by adding certain elements to the steel or by subjecting it to specific heat treatments. The goal is to produce steel that is more resistant to corrosion, which helps to extend the life of the steel in various applications.
Sensitization of stainless steel occurs when stainless steel is heated to between
1100°F-1560°F (600°C to 850°C).
Causing precipitation of chromium carbides (hard and brittle) at the grain boundaries leaving adjacent regions depleted in chromium and susceptible to intergranular corrosion.
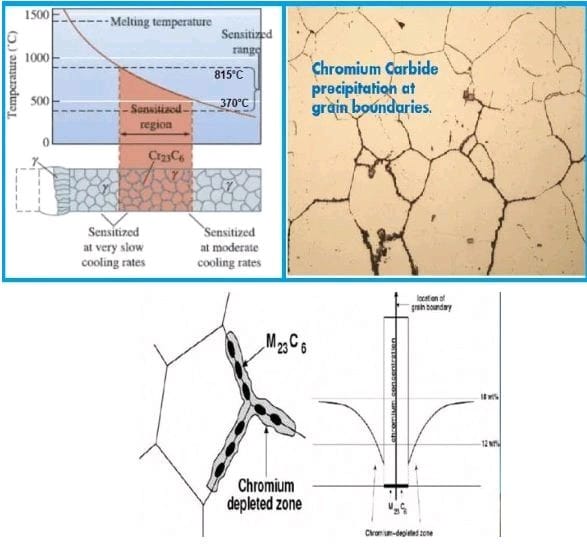
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧?
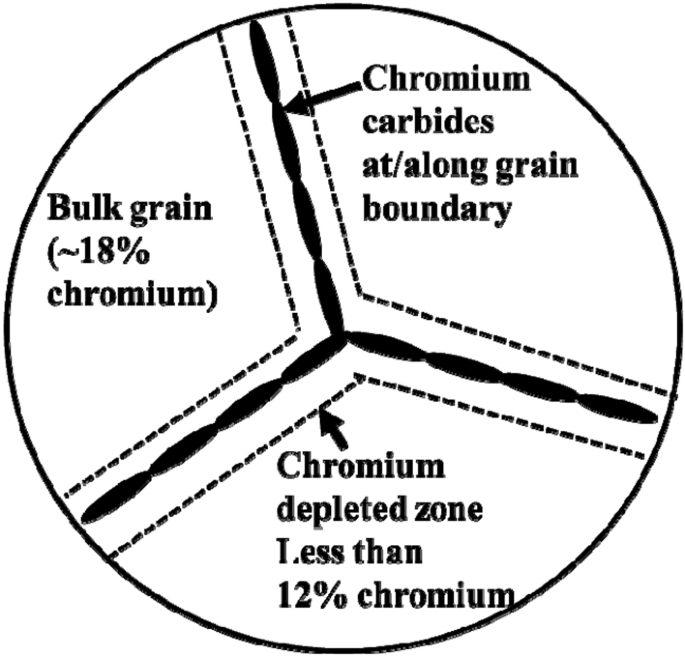
Sensitization in austenitic stainless steel refers to the phenomenon where chromium carbides form at the grain boundaries, causing a loss of chromium and a decrease in corrosion resistance. This can happen when the steel is exposed to high temperatures for prolonged periods, resulting in a reduction of its resistance to intergranular corrosion. To prevent sensitization, proper heat treatment and selection of proper alloys can be used to maintain the corrosion resistance of the steel.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐭𝐨 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐟 𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐥𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐞𝐥?
To prevent sensitization of stainless steel, the following steps can be taken:
Use proper heat treatment: Avoid high-temperature exposure for extended periods of time during the fabrication process.
Choose the right alloy: Certain alloys, such as those with high nickel or molybdenum content, are less susceptible to sensitization.
Control cooling rate: Rapid cooling can promote the formation of chromium carbides, so controlling the cooling rate can help prevent sensitization.
Avoid welding: Welding can cause sensitization, so it’s important to minimize it as much as possible. If welding is necessary, using proper techniques and filler materials can help minimize sensitization.
Use protective coatings: Applying protective coatings, such as paint or plating, can help prevent corrosion and thus minimize the effects of sensitization.
How 𝐓𝐨 𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐯𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧?

To remove the effects of sensitization in austenitic stainless steel, the following steps can be taken:
Solution Annealing: This is a heat treatment process that dissolves chromium carbides and restores the steel’s corrosion resistance.
Pickling and Passivation: This involves using a chemical bath to remove surface contaminants and oxide films from the steel’s surface, restoring its protective passive layer.
Weld Repairs: If the sensitization is localized and limited to a specific area, repairing the affected area through welding with proper techniques and filler materials can restore the steel’s corrosion resistance.
Read More :
316 Stainless Steel-Material, Properties, Composition, Uses: Grade 316 stainless steel is a highly versatile material with excellent chemical, physical, and mechanical properties. Learn about its uses, corrosion resistance, welding techniques, machining processes, mechanical properties, and more in this comprehensive blog created by Newzel Industries.
ASTM A480 Material: What It Is, Why It’s Widely Used, And Its Main Purpose? : ASTM A480 Material is general-purpose steel that can be used in many different applications. Do you need to know the difference between A470 and A480? Read this post to find out more!


