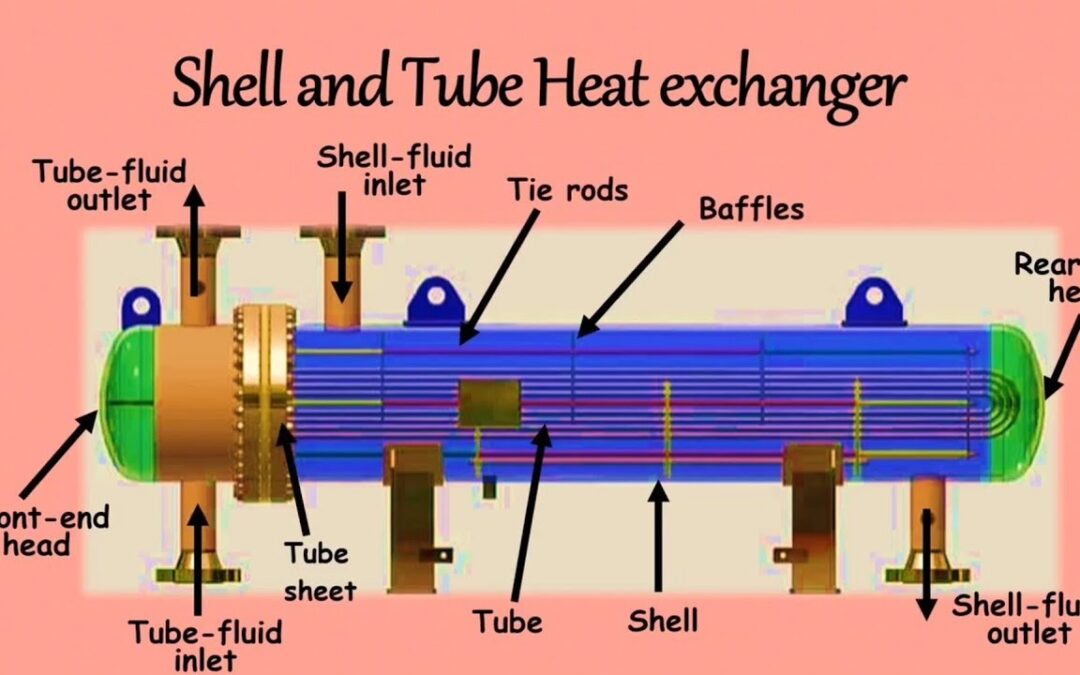
Choosing the proper materials for shell and tube heat exchangers is critical for performance and longevity. Here is a simple guide to help you make educated decisions:
Key Factors:
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential to prevent material degradation.
- Thermal Conductivity: Higher conductivity means better heat transfer.
- Mechanical Strength: Must withstand operating pressures and temperatures.
- Ease of Fabrication and Maintenance: Simplifies construction and upkeep.
- Cost: Balance between performance and budget.
Common Materials:
Carbon Steel
- Use: Non-corrosive fluids, moderate temperatures.
- Pros: Strong, affordable.
- Cons: Needs protection against corrosion.
Stainless Steel
- Grades: 304, 316, 316L.
- Use: Corrosive environments, high temperatures.
- Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, strong.
- Cons: More expensive.
Duplex Stainless Steel
- Grades: 2205, 2507.
- Use: Highly corrosive settings.
- Pros: Combines strength and corrosion resistance.
- Cons: Higher cost, specialized fabrication.
Nickel Alloys
- Grades: Inconel 600, Hastelloy C276.
- Use: Extreme corrosion and high temperatures.
- Pros: Exceptional durability.
- Cons: Very high cost.
Copper Alloys
- Grades: Admiralty Brass, Copper-Nickel.
- Use: Marine, HVAC systems.
- Pros: Good heat transfer, moderate corrosion resistance.
- Cons: Prone to localized corrosion.
Titanium
- Use: Seawater, aggressive chemicals.
- Pros: Outstanding corrosion resistance, lightweight.
- Cons: Expensive, difficult to fabricate.
Application-Based Selection Chemical Processing
- Tubes: Stainless Steel, Duplex, Nickel Alloys.
- Shell: Carbon Steel (with lining), Stainless Steel. Power Generation
Power Generation
- Tubes: Stainless Steel, Copper Alloys.
- Shell: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel.
Marine & Offshore
- Tubes: Copper-Nickel, Titanium.
- Shell: Stainless Steel, Duplex.
Petrochemical
- Tubes: Stainless Steel, Nickel Alloys.
- Shell: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Duplex.
Food & Beverage
- Tubes: Stainless Steel.
- Shell: Stainless Steel.
Conclusion
When selecting heat exchanger materials, environmental and operational considerations must be carefully considered. By balancing corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, ease of manufacture, and cost, you may ensure efficient and dependable performance. This deliberate approach not only increases the lifespan of your heat exchangers, but also improves their efficiency and dependability.